Transcript Assembly Visualization
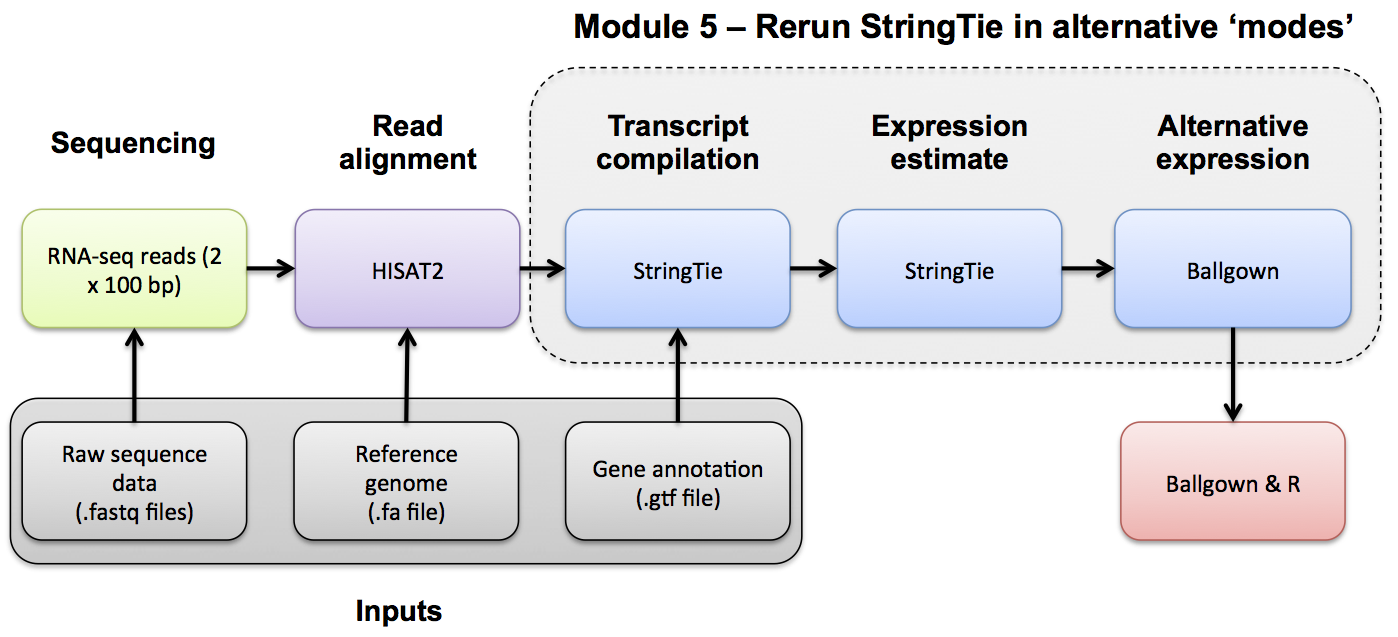
Visualizing Results at the Command Line
View the merged GTF file from the ‘de_novo’ mode. Remember this merged GTF file combines both UHR and HBR (GTFs for each individually were also produced earlier).
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/de_novo/
head stringtie_merged.gtf
For details on the format of these files, refer to the following links:
- https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/stringtie/gff.shtml#gffcompare
- https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/stringtie/gffcompare.shtml#output-files
- http://cole-trapnell-lab.github.io/cufflinks/cuffmerge/index.html
- http://cole-trapnell-lab.github.io/cufflinks/cuffcompare/index.html#transfrag-class-codes
How many genes have at least one transcript assembled by StringTie in the ‘de_novo’ results?
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/de_novo/
cat stringtie_merged.gtf | perl -ne 'if ($_ =~ /gene_id\s+\"(\S+)\"\;/){print "$1\n"}' | sort | uniq | wc -l
How many genes have at least one potentially novel transcript assembled?
head gffcompare.stringtie_merged.gtf.tmap
grep "j" gffcompare.stringtie_merged.gtf.tmap
grep "j" gffcompare.stringtie_merged.gtf.tmap | cut -f 1 | sort | uniq | wc -l
Display the transcripts that correspond to intergenic regions with the highest read support (candidate novel regions of transcription)
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/de_novo
grep -w "u" gffcompare.stringtie_merged.gtf.tmap | sort -n -k 10 | column -t
Using RegTools to annotate all individual splice junctions
RegTools is a utility we created to help characterize individual exon splicing events and help to identify novel splice events and variants that have a direct influence on gene expression or splicing patterns. Refer to the RegTools manual for more details.
We will use basic functionality of RegTools to extract a junction.bed file for each of our BAMs that summarizes all distinct exon-exon splicing events represented in the RNA-seq data. We will also use RegTools to annotate these junctions relative to our reference transcriptome GTF file:
cd $RNA_HOME/alignments/hisat2
regtools junctions extract -s RF HBR.bam > HBR.junctions.bed
head HBR.junctions.bed
regtools junctions annotate HBR.junctions.bed $RNA_REF_FASTA $RNA_REF_GTF > HBR.junctions.anno.bed
head HBR.junctions.anno.bed
regtools junctions extract -s RF UHR.bam > UHR.junctions.bed
head UHR.junctions.bed
regtools junctions annotate UHR.junctions.bed $RNA_REF_FASTA $RNA_REF_GTF > UHR.junctions.anno.bed
head UHR.junctions.anno.bed
Now pull out any junctions from either sample that appear to involve novel exon skipping, acceptor site usage, or donor site usage (relative to the reference transcriptome GTF). Require at three reads of support for each of the potentially novel junctions.
grep -P -w "NDA|A|D" HBR.junctions.anno.bed | perl -ne 'chomp; @l=split("\t",$_); if ($l[4] > 3){print "$_\n"}'
grep -P -w "NDA|A|D" UHR.junctions.anno.bed | perl -ne 'chomp; @l=split("\t",$_); if ($l[4] > 3){print "$_\n"}'
Organize illustrative GTF files to view
Note that when using StringTie in the de novo mode we get a GTF file that is based only on information obtained by examining alignments of RNA-seq reads against the reference genome. For our relatively low coverage RNA-seq data we anticipate that some transcripts will not be completely assembled accurately, others may be missed all together. In the reference only and reference guided modes StringTie has access to the reference Ensembl GTF transcriptome. This increases the sensitivity. However, when a reference GTF is available, StringTie places all of the reference transcript information in the resulting GTF, even if no evidence is found in our RNA-seq data. We need to look at the expression value predictions for each transcript to know whether there was actually any evidence found for each known transcript.
To make it easier to compare the output of the ref-only, ref-guided, and de novo results, we will now produce filtered versions of our merged GTF files where we remove transcripts unless there was some evidence for their expression.
cd $RNA_HOME/student_tools
wget https://github.com/griffithlab/rnabio.org/raw/master/assets/scripts/stringtie_filter_gtf.pl
chmod +x stringtie_filter_gtf.pl
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/ref_only/
$RNA_HOME/student_tools/stringtie_filter_gtf.pl --expression_metric=FPKM --result_dirs='HBR_Rep1,HBR_Rep2,HBR_Rep3,UHR_Rep1,UHR_Rep2,UHR_Rep3' --input_gtf_file='~/workspace/rnaseq/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf' --filtered_gtf_file='~/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/ref_only/chr22_with_ERCC92.filtered.gtf' --exp_cutoff=0 --min_sample_count=2
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/ref_guided_merged/
$RNA_HOME/student_tools/stringtie_filter_gtf.pl --expression_metric=FPKM --result_dirs='HBR_Rep1,HBR_Rep2,HBR_Rep3,UHR_Rep1,UHR_Rep2,UHR_Rep3' --input_gtf_file='~/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/ref_guided/stringtie_merged.gtf' --filtered_gtf_file='~/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/ref_guided/stringtie_merged.filtered.gtf' --exp_cutoff=0 --min_sample_count=2
Rename some GTF files generated by various approaches and place them all in a single directory for convenience when loading into IGV.
cd $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie
mkdir visualization
cd visualization
cat $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf | perl -ne 'chomp; @l=split("\t", $_); print "$_\n" unless ($l[2] eq "gene");' > chr22_reference.gtf
cp $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/ref_only/chr22_with_ERCC92.filtered.gtf ref_only.gtf
cp $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/ref_guided/stringtie_merged.filtered.gtf ref_guided.gtf
cp $RNA_HOME/expression/stringtie/de_novo/stringtie_merged.gtf de_novo.gtf
- Identify some candidate novel transcripts to visualize
Visualizing Results in the IGV Browser
merged.gtf files:
- Before loading your BAM files, make turn on the ‘Show junction track’ option (View -> Preferences -> Alignments).
- View the grand merged.gtf files that were generated by each of the StringTie modes: ‘ref_guided’, ‘de_novo’.
- Note: For the ‘ref_only’ mode, only the supplied transcript were considered. Therefore the gtf file from any individual stringtie (unmerged) will be the same and serve for comparison.
- The following can be loaded directly in IGV by url
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/visualization/chr22_reference.gtf
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/visualization/ref_only.gtf
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/visualization/ref_guided.gtf
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/expression/stringtie/visualization/de_novo.gtf
Load the BAM files at the same time as the junctions.bed and merged.gtf files:
- The following can be loaded directly in IGV by url
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/alignments/hisat2/UHR.bam
- http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/workspace/rnaseq/alignments/hisat2/HBR.bam
Go to the following regions:
- chr22:44,292,789-44,341,778 (novel 5’ exon)
- chr22:41,679,566-41,689,409 (alternative isoforms; create a Sashimi plot of this region)
- chr22:50,083,265-50,086,732 (alternative isoforms; create a Sashimi plot of this region)
- chr22:50,466,553-50,467,472 (novel cassette exon; create a Sashimi plot of this region)
- chr22:39,313,011-39,314,398 (skipping of a known exon; create a Sashimi plot of this region)
- chr22:46,362,928-46,364,315 (alternative acceptor sites; create a Sashimi plot of this region)
- chr22:18,935,247-18,953,963 (novel transcribed region)
Do you see the evidence for any novel exons/transcript that are found in ‘de_novo’ or ‘ref_guided’ modes but NOT found in ‘ref_only’ mode? Explore in IGV for other examples of novel or different transcript predictions from the different cufflinks modes. Pay attention to how the predicted transcripts line up with known transcripts. Try loading the Ensembl transcripts track (File -> Load from Server).
NOTE: We have obviously just scratched the surface exploring these output files.
