Alignment QC
Alignment QC mini lecture
If you would like a refresher on alignment QC, we have made a mini lecture briefly covering the topic.
Use samtools and FastQC to evaluate the alignments
Use samtools view to see the format of a SAM/BAM alignment file
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
samtools view -H UHR.bam
samtools view UHR.bam | head
samtools view UHR.bam | head | column -t | less -S
Try filtering the BAM file to require or exclude certain flags. This can be done with samtools view -f -F options
-f INT required flag -F INT filtering flag
“Samtools flags explained”
Try requiring that alignments are ‘paired’ and ‘mapped in a proper pair’ (=3). Also filter out alignments that are ‘unmapped’, the ‘mate is unmapped’, and ‘not primary alignment’ (=268)
samtools view -f 3 -F 268 UHR.bam | head | column -t | less -S
Now require that the alignments be only for ‘PCR or optical duplicate’. How many reads meet this criteria? Why?
samtools view -f 1024 UHR.bam | head
Use samtools flagstat to get a basic summary of an alignment. What percent of reads are mapped? Is this realistic? Why?
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
mkdir flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep1.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep2.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep2.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep3.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep3.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep1.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep2.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep2.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep3.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep3.bam.flagstat
# Note that we could have created and run a samtools flagstat command for all files ending in *Rep*.bam using the following construct:
# find *Rep*.bam -exec echo samtools flagstat {} \> flagstat/{}.flagstat \; | sh
# View an example
cat flagstat/UHR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
Details of the SAM/BAM format can be found here: http://samtools.sourceforge.net/SAM1.pdf
Using FastQC
You can use FastQC to perform basic QC of your BAM file (See Pre-alignment QC). This will give you output very similar to when you ran FastQC on your fastq files.
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
fastqc UHR_Rep1.bam UHR_Rep2.bam UHR_Rep3.bam HBR_Rep1.bam HBR_Rep2.bam HBR_Rep3.bam
mkdir fastqc
mv *fastqc.html fastqc/
mv *fastqc.zip fastqc/
Using Picard
You can use Picard to generate RNA-seq specific quality metrics and figures
# Generating the necessary input files for picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics
cd $RNA_HOME/refs
# Create a .dict file for our reference
java -jar $PICARD CreateSequenceDictionary -R chr22_with_ERCC92.fa -O chr22_with_ERCC92.dict
# Create a bed file of the location of ribosomal sequences in our reference (first extract from the gtf then convert to bed)
# Note that here we pull all the "rrna" transcripts from the GTF. This is a good strategy for the whole transcriptome ...
# ... but on chr22 there is very little "rrna" content, leading to 0 coverage for all samples, so we are also adding a single protein coding ribosomal gene "RRP7A" (normally we would not do this)
grep --color=none -i -P "rrna|rrp7a" chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf > ref_ribosome.gtf
gff2bed < ref_ribosome.gtf > ref_ribosome.bed
# Create interval list file for the location of ribosomal sequences in our reference
java -jar $PICARD BedToIntervalList -I ref_ribosome.bed -O ref_ribosome.interval_list -SD chr22_with_ERCC92.dict
# Create a genePred file for our reference transcriptome
gtfToGenePred -genePredExt chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf chr22_with_ERCC92.ref_flat.txt
# reformat this genePred file
cat chr22_with_ERCC92.ref_flat.txt | awk '{print $12"\t"$0}' | cut -d$'\t' -f1-11 > tmp.txt
mv tmp.txt chr22_with_ERCC92.ref_flat.txt
cd $RNA_HOME/alignments/hisat2/
mkdir picard
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo java -jar $PICARD CollectRnaSeqMetrics I={} O=picard/{}.RNA_Metrics REF_FLAT=$RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.ref_flat.txt STRAND=SECOND_READ_TRANSCRIPTION_STRAND RIBOSOMAL_INTERVALS=$RNA_HOME/refs/ref_ribosome.interval_list \; | sh
RSeQC [optional]
Background: RSeQC is a tool that can be used to generate QC reports for RNA-seq. For more information, please check: RSeQC Tool Homepage
Files needed:
- Aligned bam files
- Index file for each bam file.
- A transcript bed file (in bed12 format).
cd $RNA_HOME/refs/
# Convert Gtf to genePred
gtfToGenePred chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf chr22_with_ERCC92.genePred
# Convert genPred to bed12
genePredToBed chr22_with_ERCC92.genePred chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
mkdir rseqc
geneBody_coverage.py -i UHR_Rep1.bam,UHR_Rep2.bam,UHR_Rep3.bam -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/UHR
geneBody_coverage.py -i HBR_Rep1.bam,HBR_Rep2.bam,HBR_Rep3.bam -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/HBR
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo inner_distance.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/{} \; | sh
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo junction_annotation.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/{} \; | sh
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo junction_saturation.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/{} \; | sh
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo read_distribution.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 \> rseqc/{}.read_dist.txt \; | sh
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo RNA_fragment_size.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 \> rseqc/{}.frag_size.txt \; | sh
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo bam_stat.py -i {} \> {}.bam_stat.txt \; | sh
rm -f log.txt
MultiQC
We will now use multiQC to compile a QC report from all the QC tools above.
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
multiqc ./
MultiQC screenshot
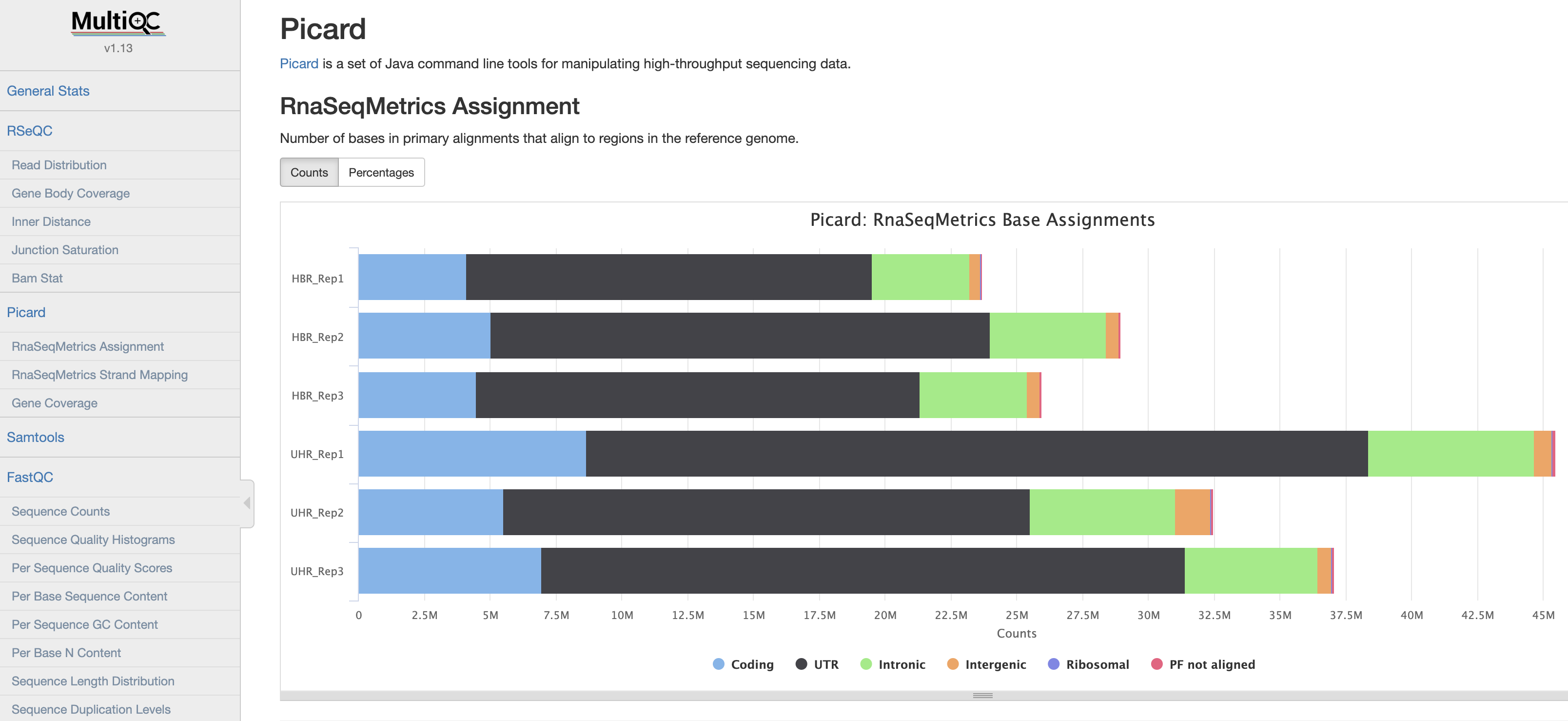
View a pre-generated MultiQC report for full bam files
View a multiQC on QC reports from non-downsampled bam files:
mkdir $RNA_ALIGN_DIR/example_QC
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR/example_QC
wget http://genomedata.org/rnaseq-tutorial/multiqc_report.html
Below is a brief description of each of the samples included in the multiQC report.
| Name | Sample type |
|---|---|
| Sample 1 | Brain metastasis |
| Sample 2 | Melanoma xenograft |
| Sample 3 | Melanoma cell line |
| Sample 4 | Melanoma |
| Sample 5 | Small Cell Lung Cancer FFPE |
| Sample 6 | Brain metastasis |
