Alignment QC
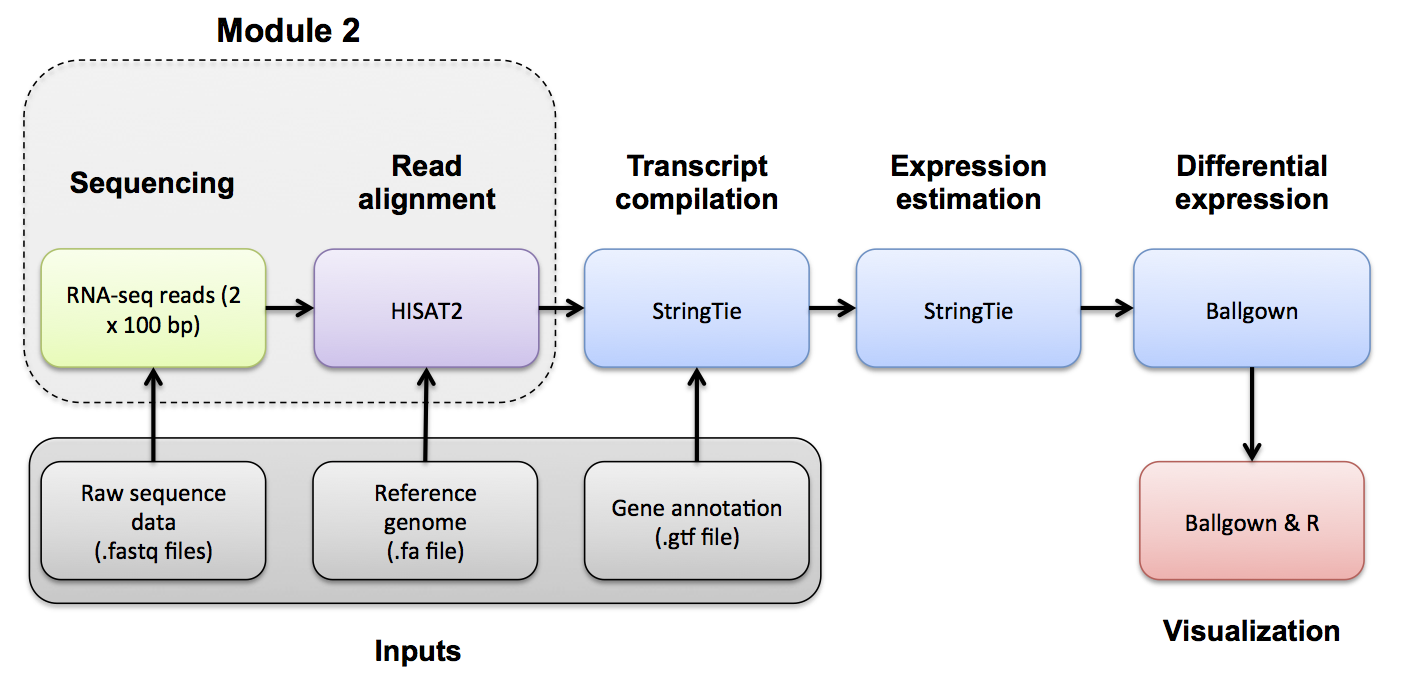
Alignment QC mini lecture
If you would like a refresher on alignment QC, we have made a mini lecture briefly covering the topic.
Use samtools and FastQC to evaluate the alignments
Use samtools view to see the format of a SAM/BAM alignment file
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
samtools view -H UHR.bam
samtools view UHR.bam | head
samtools view UHR.bam | head | column -t | less -S
Try filtering the BAM file to require or exclude certain flags. This can be done with samtools view -f -F options
-f INT required flag -F INT filtering flag
“Samtools flags explained”
Try requiring that alignments are ‘paired’ and ‘mapped in a proper pair’ (=3).
Also filter out alignments that are ‘unmapped’, the ‘mate is unmapped’, and ‘not primary alignment’ (=268)
samtools view -f 3 -F 268 UHR.bam | head | column -t | less -S
Now require that the alignments be only for ‘PCR or optical duplicate’. How many reads meet this criteria? Why?
samtools view -f 1024 UHR.bam | head
Use samtools flagstat to get a basic summary of an alignment. What percent of reads are mapped? Is this realistic? Why?
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
mkdir flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep1.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep2.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep2.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat HBR_Rep3.bam > flagstat/HBR_Rep3.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep1.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep2.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep2.bam.flagstat
samtools flagstat UHR_Rep3.bam > flagstat/UHR_Rep3.bam.flagstat
# Note that we could have created and run a samtools flagstat command for all files ending in *Rep*.bam using the following construct:
# find *Rep*.bam -exec echo samtools flagstat {} \> flagstat/{}.flagstat \; | sh
# View an example
cat flagstat/UHR_Rep1.bam.flagstat
Details of the SAM/BAM format can be found here: http://samtools.sourceforge.net/SAM1.pdf
Create versions of our BAM files with only the chromosome 22 alignments
Note that our alignments contain those for the spiked in ERCC control sequences. For some QC analyses, these sequences complicate interpretation because they are not like human genes (e.g. no introns or UTRs). To allow us flexibility for the QC analysis we will create a version of each BAM file that only has the chromosome 22 alignments.
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
mkdir chr22_only_bams
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo samtools view -b {} 22 -o chr22_only_bams/{} \; | sh
samtools index -M chr22_only_bams/*.bam
Using FastQC
You can use FastQC to perform basic QC of your BAM file (See Pre-alignment QC). This will give you output very similar to when you ran FastQC on your fastq files.
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
fastqc UHR_Rep1.bam UHR_Rep2.bam UHR_Rep3.bam HBR_Rep1.bam HBR_Rep2.bam HBR_Rep3.bam
mkdir fastqc
mv *fastqc.html fastqc/
mv *fastqc.zip fastqc/
Using Picard
You can use Picard to generate RNA-seq specific quality metrics and figures
In this section we need to create some additional formats of our reference transcriptome files.
Picard uses a “sequence dictionary” file for many commands (simply a list of reference sequences and their sizes)
We will also filter our transcriptome GTF to one with only ribosomal features, convert it to BED format and then to IntervalList format. This is all done to get the IntervalList format needed for Picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics
We will also create a version of our whole transcriptome GTF in the RefFlat format needed for Picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics. To get to the RefFlat format we will convert GTF to GenePredExt format and then simplify this to RefFlat.
# Generating the necessary input files for picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics
cd $RNA_HOME/refs
# Create a .dict file for our reference
java -jar $PICARD CreateSequenceDictionary -R chr22_with_ERCC92.fa -O chr22_with_ERCC92.dict
# Create a bed file of the location of ribosomal sequences in our reference (first extract them from the GTF then convert to BED format)
# Note that here we pull all the "rrna" transcripts from the GTF. This is a good strategy for the whole transcriptome ...
# ... but on chr22 there is very little "rrna" content, leading to 0 coverage for all samples, so we are also adding a single protein coding ribosomal gene "RRP7A" (normally we would not do this)
# Note the convert2bed command will convert our GTF to BED format
# "<" is used to feed the GTF file into the tool. ">2/dev/null" is used to throw away a harmless warning. "1>" is use to save our result to a file
grep --color=none -i -P "rrna|rrp7a" chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf > ref_ribosome.gtf
convert2bed --input=gtf --output=bed < ref_ribosome.gtf 2>/dev/null 1>ref_ribosome.bed
# Create interval list file for the location of just the ribosomal sequences in our reference
java -jar $PICARD BedToIntervalList -I ref_ribosome.bed -O ref_ribosome.interval_list -SD chr22_with_ERCC92.dict
# Create a genePred file for our whole reference transcriptome
gtfToGenePred -genePredExt chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf chr22_with_ERCC92.genePredExt
# Reformat this genePred file to first add the Ensembl gene ID column to the beginning of the dataframe using "awk", and then subset it down to the first 11 columns using "cut".
cat chr22_with_ERCC92.genePredExt | awk '{print $12"\t"$0}' | cut -d$'\t' -f1-11 > chr22_with_ERCC92.refFlat.txt
# Use the "find" command to run "picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics" on all 6 BAM files.
# The basic structure of this kind of automation is: find <search pattern> -exec command {} \;
# The "{}" will insert the file found by the "find" command using <search pattern>. "\;" indicates the end of the command.
cd $RNA_HOME/alignments/hisat2/
mkdir picard
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo java -jar $PICARD CollectRnaSeqMetrics I={} O=picard/{}.RNA_Metrics REF_FLAT=$RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_with_ERCC92.refFlat.txt STRAND=SECOND_READ_TRANSCRIPTION_STRAND RIBOSOMAL_INTERVALS=$RNA_HOME/refs/ref_ribosome.interval_list \; | sh
RSeQC [optional]
Background: RSeQC is a tool that can be used to generate QC reports for RNA-seq. For more information, please check: RSeQC Tool Homepage
Files needed:
- Aligned bam files
- Index file for each bam file.
- A transcript bed file (in bed12 format).
cd $RNA_HOME/refs/
# Convert GTF to genePred
gtfToGenePred chr22_with_ERCC92.gtf chr22_with_ERCC92.genePred
# Convert genePred to BED12
genePredToBed chr22_with_ERCC92.genePred chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12
# Create a version of the BED12 with the ERCC92 sequences removed (because they confuse the QC analysis that looks at how many reads are coding, UTR, intronic, etc.
grep -v ERCC chr22_with_ERCC92.bed12 > chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
mkdir rseqc
geneBody_coverage.py -i chr22_only_bams/UHR_Rep1.bam,chr22_only_bams/UHR_Rep2.bam,chr22_only_bams/UHR_Rep3.bam -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/UHR
geneBody_coverage.py -i chr22_only_bams/HBR_Rep1.bam,chr22_only_bams/HBR_Rep2.bam,chr22_only_bams/HBR_Rep3.bam -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/HBR
# Calculate the inner distance of RNA-seq fragments.
# RNA fragment
# _________________||_________________
# | |
# | |
# ||||||||||------------------||||||||||
# read_1 inner_distance read_2
#
# fragment size = read_1 + inner_distance + read_2
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo inner_distance.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 -o rseqc/{} \; | sh
# Annotate exon-exon junctions observed in RNA-seq alignments compared to know exon-exon junctions
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR/chr22_only_bams
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo junction_annotation.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 -o ../rseqc/{} \; | sh
# Perform a saturation analysis using only exon-exon junction mapping reads
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo junction_saturation.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 -o ../rseqc/{} \; | sh
# Determine the distribution of reads with respect to the parts of transcripts they align to (e.g. 5' UTR, CDS, 3'UTR, intron, etc.)
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo read_distribution.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 \> ../rseqc/{}.read_dist.txt \; | sh
# Calculate the RNA fragment sizes and produce statistics for each transcript
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo RNA_fragment_size.py -i {} -r $RNA_HOME/refs/chr22_without_ERCC92.bed12 \> rseqc/{}.frag_size.txt \; | sh
# Summarizing mapping statistics of each BAM file
find *Rep*.bam -exec echo bam_stat.py -i {} \> rseqc/{}.bam_stat.txt \; | sh
rm -f log.txt
MultiQC
We will now use multiQC to compile a QC report from all the QC tools above.
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR
multiqc ./
MultiQC screenshot
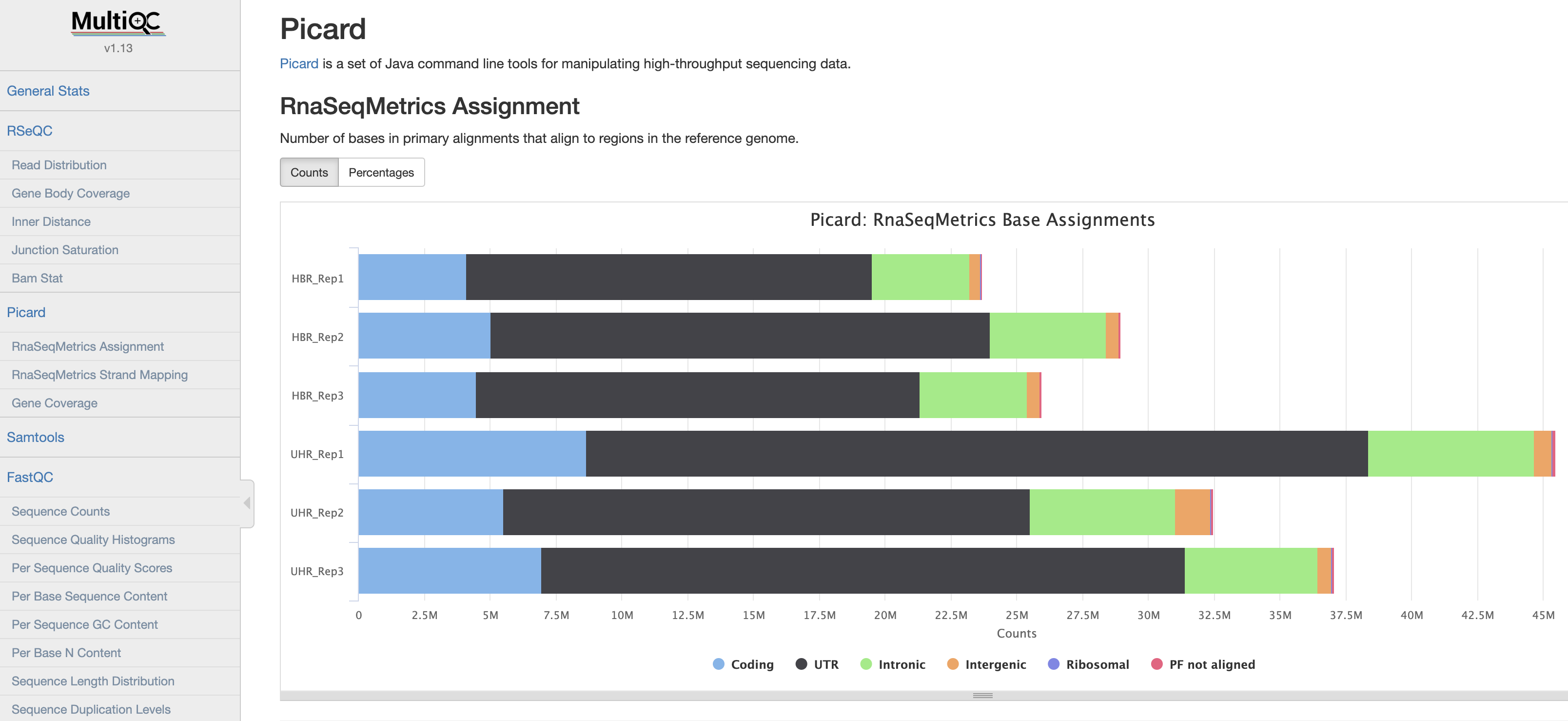
View a pre-generated MultiQC report for full bam files
View a multiQC on QC reports from non-downsampled bam files:
mkdir $RNA_ALIGN_DIR/example_QC
cd $RNA_ALIGN_DIR/example_QC
wget http://genomedata.org/rnaseq-tutorial/multiqc_report.html
Below is a brief description of each of the samples included in the multiQC report.
| Name | Sample type |
|---|---|
| Sample 1 | Brain metastasis |
| Sample 2 | Melanoma xenograft |
| Sample 3 | Melanoma cell line |
| Sample 4 | Melanoma |
| Sample 5 | Small Cell Lung Cancer FFPE |
| Sample 6 | Brain metastasis |
